Webhook Events in AI Integration: Types and Applications
Make use of webhook events in AI integration! These tools, which respond to events, use HTTP APIs to automatically manage communication between applications. This makes workflows simpler and makes processes run more smoothly. This article covers the various kinds of webhook events and their uses, such as improving GitOps methods. Learn how to use webhooks to make the most of them in live data tasks and automated processes. Change your method of application programming dramatically!
Key Takeaways:
- Webhooks are a useful way to connect AI with different apps, allowing for immediate data handling and automatic processes.
- Knowing the different kinds of webhook events-those based on data, actions, or regular intervals-is key to setting them up correctly.
- Setting up webhooks needs careful planning for security and dealing with errors, while also being aware of upcoming trends and possible issues.
- 1 Types of Webhook Events
- 2 Applications of Webhook Events in AI
- 3 AI Webhooks in Business Integrations
- 4 Best Practices for Implementing Webhooks
- 5 Case Studies
- 6 Future Trends in Webhook Integration
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions
- 7.1 1. What are Webhook Events in AI Integration and why are they important?
- 7.2 2. What are the different types of Webhook Events in AI Integration?
- 7.3 3. How are Webhook Events used in AI Integration?
- 7.4 4. Can Webhook Events be customized for specific applications?
- 7.5 5. What are some real-world applications of Webhook Events in AI Integration?
- 7.6 6. How do I set up Webhook Events in my AI Integration?
1. Definition and Purpose
A webhook is a user-defined HTTP callback that allows one application to send real-time data to another when a specific event occurs, utilizing payload data structured in JSON or XML.
For example, in GitHub, you can create a webhook to send code to a server automatically whenever code is pushed to a repository.
To configure this, open your GitHub repository, select ‘Settings’, then choose ‘Webhooks’, and type in a webhook URL that connects to your server for deploying.
Choose the event type (like ‘push’) and GitHub will send a POST request with details about the code change in JSON format. This allows your deployment tools, such as Jenkins or Travis CI, to quickly react and make your CI/CD pipeline work better.
2. Difference Between Webhooks and APIs
Unlike APIs that require periodic requests to retrieve data, webhooks send data automatically when events occur, providing a more efficient event-driven solution. This efficiency significantly reduces server load. For instance, using APIs, a server might handle multiple requests per minute, translating to hundreds or thousands of requests daily.
In contrast, webhooks trigger only when specific events happen, minimizing unnecessary traffic. Data from various applications indicate that webhooks can reduce server load by up to 90%, making them a good choice for real-time apps such as chat notifications or payment processing.
By using webhooks, developers can simplify their tasks and make sure data is sent quickly.
Types of Webhook Events
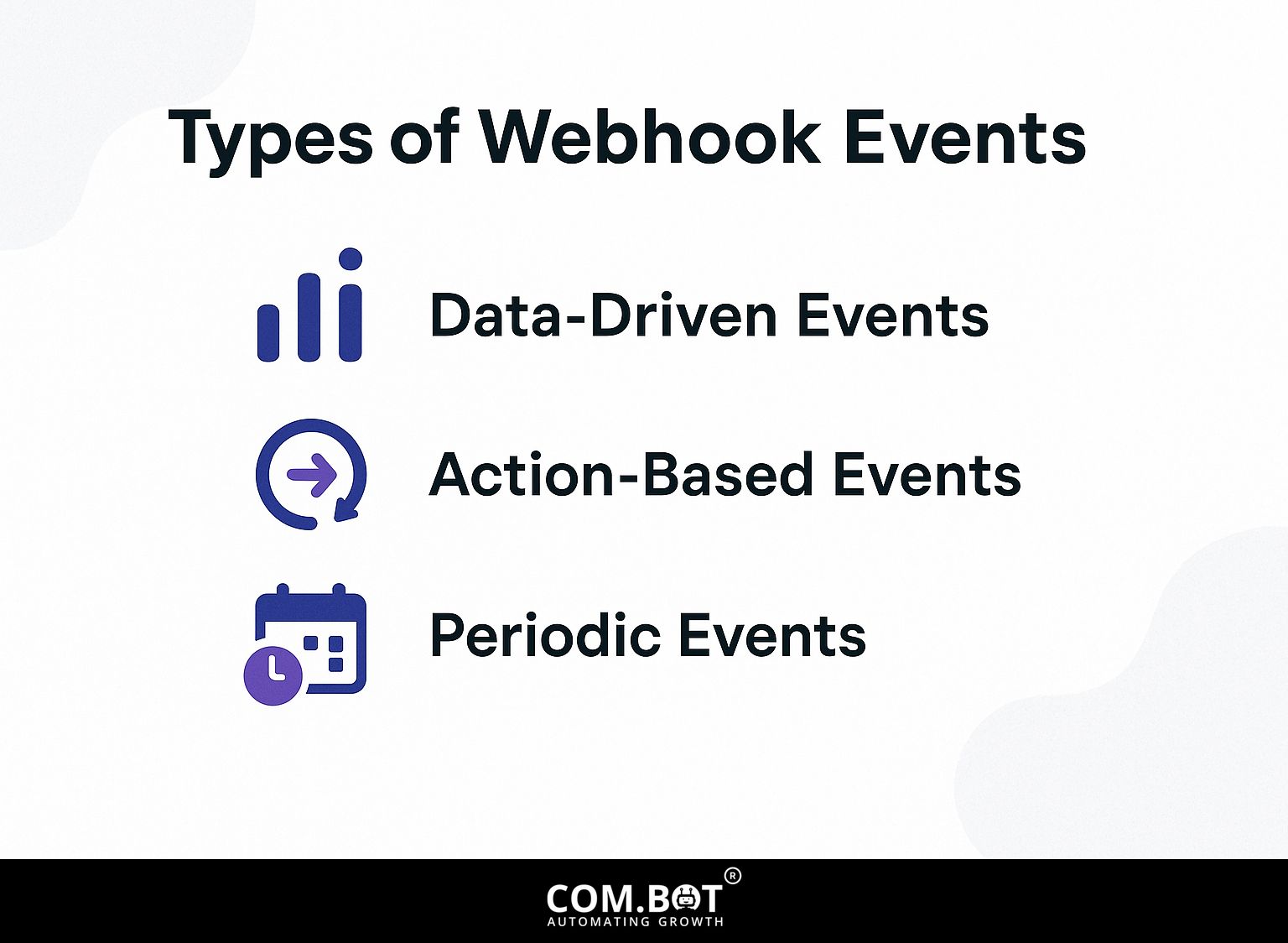
Webhook events fall into three main types, each serving different automation needs, allowing smooth data management between systems. Worth exploring: Webhook Integration with WhatsApp API: Setup
1. Data-Driven Events
Data-driven webhook events are triggered by changes in data, such as user registrations or updates, and typically transmit rich payload data in JSON or XML format.
For example, in ServiceNow, you can set up a webhook that activates when a new user registers. This event would send a JSON payload containing fields like ‘user_id’, ’email’, and ‘timestamp’.
To set this up, go to the webhook settings, make a new endpoint, and choose your event trigger (like ‘user.insert’). Use tools such as Postman to check that the webhook sends data properly. This helps connect with other apps and set up automatic workflows.
2. Action-Based Events
Action-based webhook events are initiated by user actions, such as button clicks or form submissions, leading to immediate system responses.
For instance, in an e-commerce platform, when a user completes a payment, a webhook can trigger an inventory update. This process typically requires setting up a listener endpoint that receives the payment confirmation data.
Tools like Zapier can make this easier by linking the payment processor (like Stripe) to the inventory management system (such as QuickBooks). Connecting these systems lets the inventory refresh immediately, ensuring stock levels stay accurate without manual input and helping operations work well.
3. Periodic Events
Periodic webhook events are scheduled to send data at regular intervals, useful for updates that don’t necessitate real-time transfer.
Using a scheduling tool like Zapier can improve this process by sending daily updates on project statuses through email or Slack.
For example, you can set up a Zap to connect your project management tool, like Trello or Asana, to gather tasks completed the previous day and send a brief report each morning automatically. This keeps team members informed without needing regular meetings, encourages responsibility, and makes work processes smoother.
Applications of Webhook Events in AI
Webhook events are important for AI applications because they enable quick data handling and make tasks automatic.
AI Webhooks in Business Integrations
Webhook integration can particularly enhance WhatsApp API interactions, offering seamless automation for business communications. Related insight: Webhook Integration with WhatsApp API: Setup demonstrates how these integrations can be effectively implemented.
Usage Statistics and Impact: Social Media Marketers Using Instagram
Usage Statistics and Impact: User Engagement
Usage Statistics and Impact: Fashion Brands on Instagram
Usage Statistics and Impact: Influencer and Reels Usage
The dataset on AI Webhooks in Business Integrations shows how businesses and influencers use Instagram to improve marketing plans and connect with users. Instagram is an important marketing tool, shown by the large number of social media marketers and online stores using it effectively.
Usage Statistics and Impact data indicate that 80% of social media marketers engage with Instagram for promotions, demonstrating its effectiveness in reaching targeted audiences. The platform’s popularity is evident with 86% of US-based, 81% of UK-based, and 75% of Germany-based online stores maintaining a presence on Instagram, underscoring its global influence in the e-commerce sector.
User Engagement is significantly high, with 90% of Instagram users following business accounts, illustrating the platform’s capability to connect brands with consumers. Furthermore, 62% of users show increased interest after watching Instagram Stories, highlighting how this feature can increase user engagement and brand attention.
Fashion Brands on Instagram see significant involvement, with an impressive 98% utilizing the platform. The Media Impact Value (MIV) is notably high for brands like Dior ($782 million), Chanel ($515 million), and Louis Vuitton ($55 million), reflecting Instagram’s massive role in fashion marketing and brand visibility.
Influencer and Reels Usage data reveals that 54% of nano-influencers and 33% of micro-influencers use Instagram, illustrating the platform’s diverse influencer ecosystem. Despite this, only 36% of businesses use Instagram Stories for promotion, and 53% of US marketers engage with Instagram Reels indicating potential new areas for businesses to look into these features more carefully.
The statistics highlight Instagram’s key part in current marketing plans, showing the need to keep using new features like Stories and Reels to achieve the best results. By using this information, businesses can improve their visibility and connect with their audience more effectively.
Real-Time Data Processing
Webhooks enable apps to handle live data quickly, providing instant reactions to user actions or updates in the system.
For instance, you can implement Apache Kafka to handle IoT telemetry data sent via webhooks. Start by setting up a Kafka cluster, then create a topic for your telemetry data.
In your application, configure a webhook that pushes incoming data directly to this Kafka topic. Use the Kafka Streams API to handle this data instantly, allowing fast responses to telemetry updates. This setup enables applications to grow and react quickly to new data from your IoT devices.
Automated Workflows
Webhooks can simplify tasks by linking different apps, initiating processes between them when specific events occur.
To create an automatic process with Zapier and webhooks, follow these steps:
- Start by creating a new Zap, choosing ‘Webhooks by Zapier’ as the trigger.
- Select ‘Catch Hook’ to receive data from an external source.
- For example, if you use a Google Form, configure it to send submissions to the webhook URL provided by Zapier.
- Next, in the action step, choose an app like Gmail to send an email each time a form is completed.
This reduces the time spent on entering data and allows quick communication.
Best Practices for Implementing Webhooks

To use webhooks properly, follow best practices for security and handling errors to keep them reliable and safe. For a deeper understanding, explore techniques and strategies in our hidden gem on handling messaging events with Azure.
1. Security Considerations
Securing webhook endpoints with Transport Layer Security (TLS) is essential to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Along with TLS, implement specific security measures like IP whitelisting, validating payloads, and using secret tokens.
For instance, in a GitHub webhook configuration, you can set up IP whitelisting by allowing only requests from GitHub’s IP ranges. Then, validate incoming payloads by checking for a specific signature header.
Use a secret token to sign requests, ensuring that only authorized calls reach your endpoint. These steps collectively strengthen security and help maintain the integrity of your data.
2. Error Handling
Strong error handling methods are important for webhooks to make sure events are recorded, tried again, or properly managed if something goes wrong.
To effectively manage webhook errors, implement a retry logic where failed requests are attempted again after a short delay, such as 5 seconds, with a maximum of 3 retries.
Example: If a webhook doesn’t send data to a server successfully, record the error information like the time it happened and the endpoint for later examination. Using tools like Sentry or Loggly can make logging easier.
Think about creating notifications to let your team know right away about ongoing issues, so they can look into them and fix them quickly.
Case Studies
Looking at examples of successful webhook setups shows useful tips and frequent mistakes. For those handling messaging events, leveraging platforms like Azure can be particularly beneficial. To better understand these techniques, consider exploring our guide on Handling Messaging Events with Azure: Techniques and Best Practices.
1. Successful Implementations
Successful implementations can be seen across industries, such as e-commerce platforms using webhooks for real-time inventory updates after purchases.
In the travel industry, companies like Expedia use webhooks to automatically inform users about flight status changes, providing timely updates.
In the finance sector, services like Stripe use webhooks to quickly notify about payments and make transaction processing simpler. These real-time updates improve how users interact with the system and how well businesses perform, as they allow businesses to react right away to important changes.
By using these integrations, customer satisfaction can be improved significantly, and operations can become more efficient. Webhooks are an important tool in many fields.
2. Lessons Learned
Webhook setups show that testing thoroughly and monitoring closely are important to prevent major issues.
A recent analysis showed that developers who didn’t thoroughly test their work ran into many errors because certain responses weren’t managed properly. To avoid this, implement a staged rollout:
- Start in a staging environment.
- Monitor the logs closely.
- Use tools such as Postman for simulating requests.
Set up alerting systems with services like PagerDuty, which can notify your team of webhook failures. This method quickly identifies and addresses issues, minimizing interruptions to your tasks.
Future Trends in Webhook Integration

As technology changes, webhook integration will grow, affected by new technologies and changing user needs. This evolution is particularly relevant for AI-driven applications, such as those discussed in our insights on AI-Powered Business Chat: Dashboard Features and Global Reach, which demonstrate how AI advancements are reshaping digital communication.
1. Emerging Technologies
New technologies like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and GitOps practices will improve how webhooks are managed and put into use.
Ansible, a well-known tool for infrastructure as code, can set up webhooks in different settings using YAML playbooks. For instance, you can create a playbook that defines webhook endpoints for different environments such as development, staging, and production.
By utilizing the ‘template’ module, you can manage secrets and specific configurations for each environment seamlessly. Coupling Ansible with version control (like Git) allows for tracking changes and rollbacks in webhook configurations. This method simplifies setup and reduces mistakes from manual settings.
2. Potential Challenges
Even though they have benefits, webhook integration can have problems, like dealing with growth and managing many events at once without problems.
One common challenge arises when dealing with a sudden spike in webhook events, such as Black Friday sales for an e-commerce platform. Performance can suffer if the server isn’t set up properly to manage these loads.
To address this, consider implementing a queuing system using tools like RabbitMQ or Amazon SQS. These can buffer incoming webhook events, allowing your application to process them at a manageable rate.
Using rate limiting strategies can stop your system from being overloaded and make sure important events are always handled, which improves reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are Webhook Events in AI Integration and why are they important?
Webhook Events in AI Integration are notifications that are triggered when certain conditions are met within an AI system. They are important because they enable instant updates and communication between different systems, making the integration process smoother.
2. What are the different types of Webhook Events in AI Integration?
There are two main types of Webhook Events in AI Integration: internal and external. Internal Webhook Events are triggered within the AI system itself, while external Webhook Events are triggered by external sources such as user actions or data changes.
3. How are Webhook Events used in AI Integration?
Webhook Events are used in AI Integration to trigger actions or updates in other systems. For example, an AI chatbot can use a Webhook Event to alert a customer service agent when a user requests help from a person.
4. Can Webhook Events be customized for specific applications?
Yes, Webhook Events can be customized for specific applications by setting up specific conditions and actions for each event. This makes it easier to connect the AI system with other programs in a way that fits specific needs.
5. What are some real-world applications of Webhook Events in AI Integration?
Webhook Events in AI Integration can be used in a variety of areas and applications, such as e-commerce for instant order updates, healthcare for monitoring patients, and marketing for personalized notifications and recommendations.
6. How do I set up Webhook Events in my AI Integration?
The process of setting up Webhook Events in AI Integration may vary depending on the specific systems and applications involved. Usually, this involves setting up a webhook endpoint in the system that receives the data and setting up the events and actions in the AI system to start the webhook. It is recommended to consult the documentation or support resources of the systems involved for specific instructions.